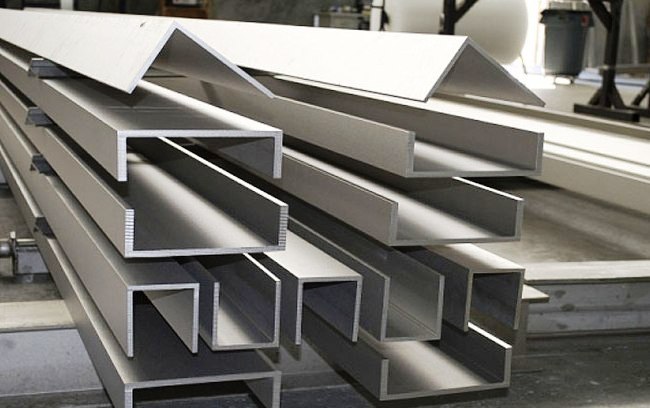
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Plastic in Construction
Plastic is now a necessary component of every day living. The amount of plastic that is consumed grows yearly. We’ll talk about everything there is to know about using plastic as a building material and whether it can alter our perception of construction in this section.
The Source
The Greek word “plastikos,” which meaning “capable of being moulded,” is where the word “plastic” originates. It is composed of flexible, long-lasting, and reasonably priced fully or semi-synthetic compounds.
While expanded polystyrene—a material created by Dow Chemical in 1954—was used for building isolation, cattle horns were utilized as lantern windows during the Middle Ages. The properties, benefits, drawbacks, and uses of plastics are being taken into consideration as times change.
In industrialized nations, one-third of plastic is utilized for packaging and as building materials for vinyl siding and plumbing. Chewing gum is one example of a naturally occurring plastic material. Later, chemically modified naturally occurring materials like natural rubber, collagen, galalite, and nitrocellulose were used to make plastics. Eventually, completely synthetic molecules like bakelite, epoxy, polyvinyl chloride, LDPE, and HDPE were used.
Plastic has a lot of benefits and is now used in many aspects of our daily life. It is also one of the most widely used construction materials too. Here, we’ll learn about the many characteristics of plastic, as well as its applications, benefits, and drawbacks, both generally and specifically in relation to the building industry.
Common Applications of Plastic in Construction
- Plumbing fixtures, pipes, and manhole covers
- Roofs
- Wall panels for dry wall or wall partitions
- electrical outlets
- furnishings such as tables and chairs, etc.
- Closets
- Layouting
- Membranes that are waterproof
- phony ceiling panels
- Sealants
- Tanks of water
Plastics are becoming more prevalent in construction even though they are bad for the environment. Let’s examine the benefits and drawbacks of plastic in detail.
Benefits of Using Plastic in Construction
There are benefits to using plastic.
- Because they don’t biodegrade, plastics are strong and can endure a long time.
- Plastics don’t lose their shape because of their exceptional strength and toughness.
- Plastics are inexpensive to make and are readily available for purchase for home construction.
- When disassembled, they can be easily reassembled with other plastics, especially for plumbing projects.
- In landfills, plastics don’t take up much room. Plastic materials take longer to decompose in a landfill than other materials, but they also occupy less space there than other materials. Paper products take up seven times the volume of plastic products.
- When plastics are disposed of in landfills, methane is not exposed to the atmosphere. Since plastics don’t release methane gas during their breakdown, it should be simpler to calculate a plastic product’s entire life cycle with accuracy. It’s practical when it comes to demolition.
- Because of their high energy density, plastics can be burned in some circumstances, making them a valuable resource.
- Because of their advantages—such as their lack of wrap, rot resistance, and lightweight nature—UPVC (Unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride) products are used in place of traditional products for cladding panels, soft boards, fascia, etc.
- Since termites cannot attack plastic decorative laminates like they can wood, they are widely used for paneling and furniture.
- By lowering dead loads, it keeps buildings from becoming too heavy when using conventional materials.
Plastic’s Drawbacks in Construction
The following are some drawbacks of plastics:
- Plastic is the primary cause of the majority of ocean pollution worldwide, and because animals of all kinds eat plastic, this pollution is killing them.
- Plastics are less expensive, but they have an impact on people’s lives, which has a higher cost.
- It is common for plastics to become softer in higher temperatures. This limits its application to hot water systems and major structural components.
- The plastic may become brittle in colder climates and shatter under pressure. Therefore, it is advised against using it in cold climates.
- Since many plastics are difficult to recycle, there is worry about how long it will take for them to break down because many of them take millions of years.
- Plastics are not appropriate for load-bearing applications, such as beams and columns, due to their low modulus of elasticity.
- Even though plastic has the ability to withstand fire, many types of plastic have a high rate of thermal expansion, necessitating greater design detail to allow for sufficient thermal movement.
Features of Plastic That Improve Its Adequacy
The benefits of plastic, which include the following, have led to an increase in its use in construction:
- Plastic’s strength and lightweight nature make it ideal for use in construction because they facilitate transportation, loading and unloading, installation, and other tasks.
- Because of its great ability to withstand weather, it is also resistant to corrosion, which means less maintenance—a crucial factor for buildings. PPS, or polyphenylene sulphide, is a chemical used in plastic for this purpose. It is primarily utilized in applications where high-temperature, highly corrosive chemicals are present.
- It can create tight seals that would prevent any liquid from passing through it to interact with another material. Put another way, its structure makes it impermeable. Polymeric chains are formed during their creation. This kind of construction has the ability to repel water, which makes the building somewhat leakproof.
- It can withstand fire. To make polyethylene for this purpose during processing, antimony trioxide is combined with a brominated compound. When combined with brominated compounds, antimony trioxide strengthens their fire-retardant qualities. The combustion process is slowed down to achieve this.
- Because of its anti-vibration qualities, plastic is flexible and can withstand significant deflections, such as those caused by earthquakes, without deforming. This leads to an improvement in the building’s seismic performance.
- Plastic has the ability to dampen vibrations. This property allows for the management of airborne noises.
- Plastic is a fantastic material for thermal insulation. This can be accomplished by adding foamed plastic sheeting to the structure.
You now have a solid understanding of plastic’s use in construction. But everyone has the same question: what will become of plastic in the future? So let’s investigate.
Potential Applications of Plastic in Construction
Building houses out of plastic is a trend that is growing in popularity these days. Various admixtures are used for this, which increases strength. Bricks made of recycled plastic are being used, and they have several benefits, including
- Minimal impact on the environment.
- Lower energy usage
- Lighter and thinner than regular bricks
- Affordable modular homes
- Buildings that are earthquake-resistant structurally
- Superior insulating qualities (approximately five times more than standard bricks)
- Excellent sound absorption
In summary
Without a doubt, the most innovative product in recent memory is plastic. Its applications in buildings are always changing as times go by, and in the future, unanticipated uses like load-bearing members or uses in different climates might occur. China is the country that produces the most plastic—nearly 60 million tonnes. The US came in second with 38 million tonnes, followed by Germany with 14.5 million and Brazil with 12 million tonnes. The use of plastic is increasing in these developed nations. Plastics will therefore be used as building materials for homes in the future.
We hope that this has given you enough knowledge to understand how plastic could be used as a building material. Here’s the next in the series on building materials you should know about before you leave.